As more aspects of life and business move online, the prevalence of spoofing attacks has surged. Despite the addition of multiple security measures, in 2023, nearly 45.6 % of all e-mails worldwide were identified as spam.
This underscores the ongoing challenge of safeguarding digital communication.
Defining Spoofing Attacks
Spoofing is misleading a communication or identity and making it look authentic. It usually takes the form of emails but spoofing involves many other forms. Most attacks impersonate the trusted relationship between the source and receiver. It can impact a person or organization with serious consequences by using their credentials.
1. Email Spoofing
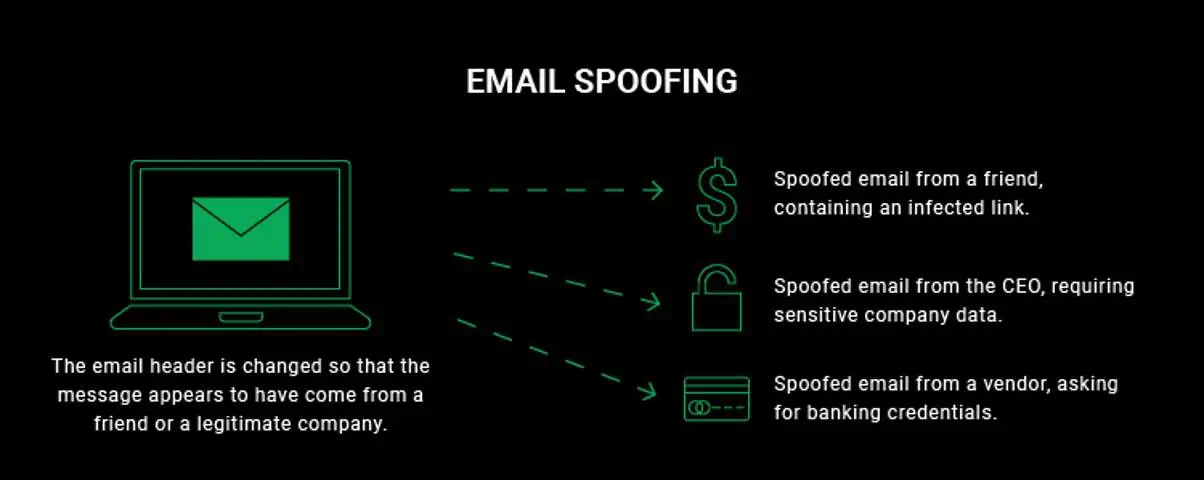
Email Spoofing is the most common type of spoofing. It involves sending emails from forged sender addresses. In this attackers aim to fool recipients into believing that email is authentic. The main goal is to lure victims into clicking a malicious URL.
Result
By distributing the malware, spoofers can steal an organization’s protected data. Malicious attachments in spoofed emails can install malware, or viruses on the victim’s device.
Example
An email, apparently from Amazon, was received by a user saying that your Amazon account will get closed due to suspicious activity. A link was provided to verify identity.
After the receiver clicked the link and added the login details, the scammer gained access to the Amazon account. It helped him make unauthorized purchases.
2. IP Address Spoofing Attacks
In this attack, a preparator disguises himself by sending IP packets from a fake IP address. The person’s true identity is concealed to mislead the target with increased data traffic. During the assault, the attacker distributes data packets to various network recipients.
Result
The recipient’s network service gets interrupted by the increased false traffic. The attacker impersonates the IP address of the device to sneak into a network.
Example
Pretending to be eBay, attackers flood eBay’s servers with too much traffic. This made eBay’s website stop working for a while and caused problems for real users, making them lose trust in eBay.
3. Caller ID Spoofing
The easiest spoofing attack is through fake calls. In this, the spoofer employs caller ID to make it seem like the call is coming from a trustworthy source. Caller ID is manipulated to look similar to the user’s number. Even the area code is manipulated to make it look familiar.
Result
After the user answers the call, the spoofer pretends that he belongs to some reputable organization asking for personal information. If the information is provided, the spoofer uses it in fraudulent activities.
Example
A scammer faked a number to look like it was from Chase Bank and called a customer. The customer, seeing Chase’s number, believed the call was real and gave away their banking details. The scammer then used this information to access and steal from the customer’s account.
4. Website Spoofing
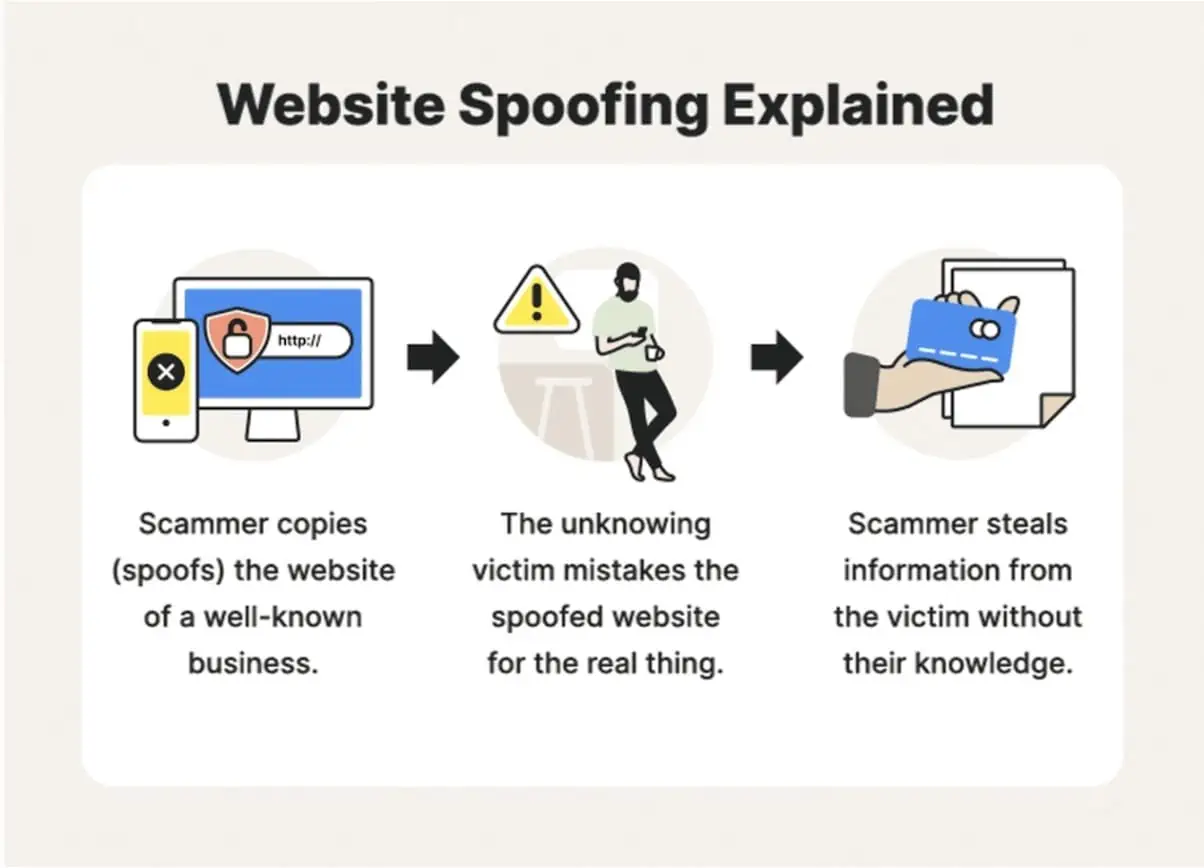
A website spoofing attack crafts a fake website to mimic a familiar, trusted website. It is mostly done with the help of other forms of spoofing after the link is shared either through SMS or email. Instead of following a sender policy framework, a falsified website is generated and sent to the victims.
These fake web addresses replicate the genuine site, which could be of brand, organization, or any named website.
Result
Victims of the scam click the URL thinking that they are using a genuine site. The website asks for login with the email address, password, and personal information in some cases. If added, this information can be used later on to hack into the email address of the user or to steal other sensitive information.
Example
Cybercriminals created a fake PayPal site that looked like the real one. It tricked users into logging in through phishing emails. This allowed the attackers to steal login details. They unauthorizedly access users’ accounts, leading to financial losses.
How To Detect Spoofing Attacks
With the advancement in technology, users now are more aware of the attacks. However, to effectively protect users from these attacks, guide them about the forms of spoofing. They must know the difference between actual and fake sources must be taught.
If looked closely, users may notice major differences. There will be a missed or different character used in the sender’s email address or a misspelt word in the URL. If there appears a pop-up asking for unusual details to log in to the account, ignore the provided link and try finding one with a genuine source.
The Impact on Small Businesses
Usually, well-established businesses manage the attacks by implementing preventive strategies. However, small businesses are affected depending on the severity of the attacks.
Some major impacts on business are:
- Businesses can face loss or manipulation of important data needed to maintain business dealings.
- If the spoofer uses the information in fraudulent activities, the brand’s image can be affected.
- If sensitive customer data is leaked, the company at fault is held accountable.
- Financial losses can arise when compensating customers who have had their personal information compromised.
- The compromise of critical assets can lead to delays, diminishing both market success and competitive edge.
The Defense Strategy
To combat spoofing and money laundering, many institutions have established different ways. Some email security software and organizations are working to provide scam-free communication channels. Yet, the drawback here is that these organizations work best for large businesses as they charge for services.
Some other ways are also devised to prevent spoofing attacks. A few of them are listed here.
Building Awareness
For spoofers, email addresses, and personal information of employees are the ultimate sources to steal information. Therefore, companies should devise ways to educate their staff about these scams. Employees should stay vigilant while sending and receiving sensitive information.
Technological Safeguards
With the advancement in technology, extra layers of security are being added to every platform. Various Anti-spoofing software are used now including PhishTitan., Avanan Email Security, and Barracuda Email Security.
Reporting and Responding to Spoofing Attacks
To effectively address spoofing attacks, companies must monitor network traffic to identify any unusual activity. There must be established protocols to report suspected activities to relevant security departments. DMARC report analyzer can help generate reports against cybercrimes.
To effectively address spoofing attacks, companies must monitor network traffic to identify any unusual activity. There must be established protocols to report suspected activities to relevant security departments. DMARC MSP solution tailored for Managed Service Providers (MSPs), will provide comprehensive tools and support for businesses seeking enhanced email security.
Conclusion
In conclusion, being aware of and prepared for spoofing attacks is essential for businesses in safeguarding their financial assets, protecting sensitive data, maintaining their reputation, and ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements.
Article and permission to publish here provided by Tatevik Iskajyan. Originally written for Supply Chain Game Changer and published on March 24, 2024.
All images provided by Tatevik Iskajyan.

